Bitcoin 101 began in 2009 when a mysterious figure named Satoshi Nakamoto introduced a concept that would eventually challenge the very foundation of how we understand money. Today, that creation—Bitcoin—has become a buzzword in newsrooms, living rooms, and boardrooms across the globe. But for many, it’s still unclear what Bitcoin actually is.
If you’ve heard the term but never fully grasped it, this Bitcoin 101 guide is for you. Consider this a neutral, down-to-earth explainer for anyone looking to understand how Bitcoin works, why it’s often compared to gold, and what role it might play in the future of global finance.
What Is Bitcoin? A Beginner’s Introduction
At its core, Bitcoin is digital money. It doesn’t come in paper form, and you can’t hold it in your hand. It exists only online, secured by cryptographic algorithms and recorded in a public ledger called the blockchain.
This isn’t just a fancy technical upgrade to existing online banking. Bitcoin was designed to operate independently of banks, governments, or any central authority. It was meant to be peer-to-peer, which means you can send it directly to someone else—no middleman, no bank, no credit card company. That vision was radical at the time, and still is.
How Bitcoin Works: The Digital Money Basics
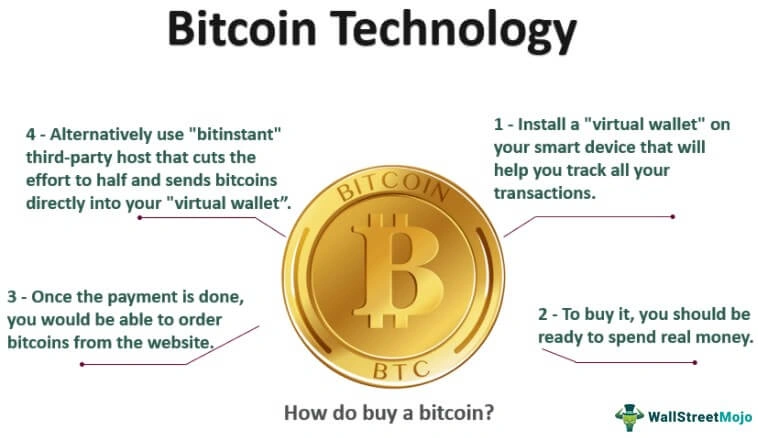
Credit from WallStreetMojo
Imagine you wanted to send $100 to a friend in another country. With a bank, that might involve transaction fees, exchange rates, and a waiting period. With Bitcoin, that same transaction can happen in minutes (sometimes seconds), with no intermediary—just your computer and theirs.
So how does it stay secure?
Every Bitcoin transaction is recorded on a blockchain, a distributed database that is maintained by thousands of computers (or “nodes”) around the world. Each time someone sends Bitcoin, that transaction is verified by these computers using complex calculations. Once verified, the transaction is added to a block, which links to previous blocks—hence, the term blockchain.
What makes Bitcoin unique is that this ledger is public and immutable. Anyone can view the full history of Bitcoin transactions, but no one can alter past records without consensus from the majority of the network.
Bitcoin Mining: The Engine Behind the Ledger
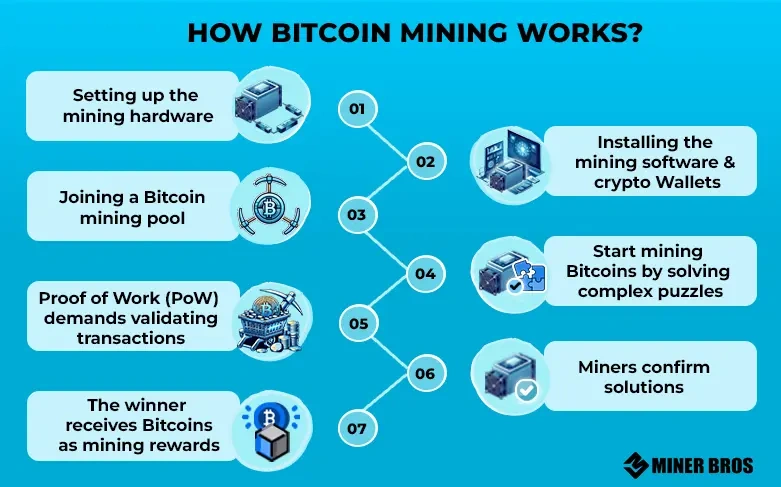
Credit from Crypto Miner Bros
You might have heard of “mining” in relation to Bitcoin. It’s a misleading term in some ways—no one is digging anything out of the ground. Instead, miners are running powerful computers to solve cryptographic puzzles. The first to solve the puzzle earns the right to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain and receives newly minted Bitcoins as a reward.
Mining was once a hobbyist’s game, but today it requires specialized hardware and consumes substantial electricity. The design is intentional—it makes the system secure and the supply of new coins predictably slow.
Only 21 million Bitcoins will ever exist. This limited supply, paired with growing demand, is part of what fuels Bitcoin’s value—and volatility.
Bitcoin for Beginners: Why It Matters
So why do people care about Bitcoin?
Some see it as a hedge against inflation—like digital gold—because its supply can’t be manipulated the way traditional currencies can. Others value it for its transparency and lack of centralized control.
Still, for many beginners, the draw of Bitcoin lies in its potential: a form of money native to the internet, borderless, and programmable. In countries with unstable banking systems, it has already become a lifeline.
And yet, it’s not perfect. Prices fluctuate wildly. Transactions, while secure, can be slower than traditional credit card payments. And let’s be honest—understanding wallets, keys, and seed phrases takes time.
But that’s what this Bitcoin 101 guide is about: peeling back the layers so newcomers can navigate this complex space with confidence.
Wallets, Keys, and Satoshis: A Quick Tour of the Basics
To use Bitcoin, you need a wallet. Think of it as a digital version of a bank account—only you’re the sole owner. There’s no recovery number to call if you forget your password. You hold your own keys, which are long strings of alphanumeric characters used to authorize transactions.
Every wallet has two types of keys:
- Public key: Like your email address, it’s safe to share.
- Private key: Like your password—never share it.
Within this system, you can own fractions of a Bitcoin. The smallest unit is called a Satoshi (0.00000001 BTC), named after its creator.
Bitcoin 101: Is Bitcoin Legal? Safe? Sustainable?
Legality varies. Bitcoin is legal in most countries, though rules around its use differ. Some governments embrace it, others ban it outright.
Security-wise, the Bitcoin network itself is extremely secure, but how individuals store and use their Bitcoin can be a weak link. Hacks typically happen at exchanges or due to human error (lost wallets, phishing scams).
Sustainability is another challenge. Mining consumes large amounts of electricity, though efforts are underway to use renewable energy and shift toward more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms in future blockchains.
Bitcoin 101: Bitcoin and the Future of Money
Whether you’re a believer or a skeptic, there’s no denying Bitcoin has sparked a global conversation about the nature of money.
Some see Bitcoin as a store of value. Others envision a world where cryptocurrencies replace or complement national currencies. Financial institutions, once wary, are now exploring Bitcoin ETFs and blockchain-based systems.
Bitcoin’s limited supply, increasing adoption, and decentralized infrastructure have led many to believe it’s not just a passing trend—but a foundational shift in how we think about finance.
Bitcoin 101: Final Thoughts
It’s not necessary to become a tech wizard to begin understanding Bitcoin. The goal of this Bitcoin 101 guide is to help you see it not as a mysterious code, but as part of an ongoing story about how we exchange value.
Whether you’re exploring how Bitcoin works, planning your first wallet setup, or just curious about its future role in the economy, learning the basics of Bitcoin is a meaningful first step.
And that’s the key: not rushing to invest or speculate, but taking the time to learn what Bitcoin is—and why it might matter far beyond the next news headline.



