Introduction
In the evolving landscape of cryptocurrency, understanding the distinction between On-chain vs Off-chain Transactions is crucial. These two methods define how transactions are processed, validated, and recorded within blockchain networks. Each has its unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations. This guide delves into the differences between on-chain and off-chain transactions, providing clarity on their roles in the crypto ecosystem.
What Are On-Chain Transactions?
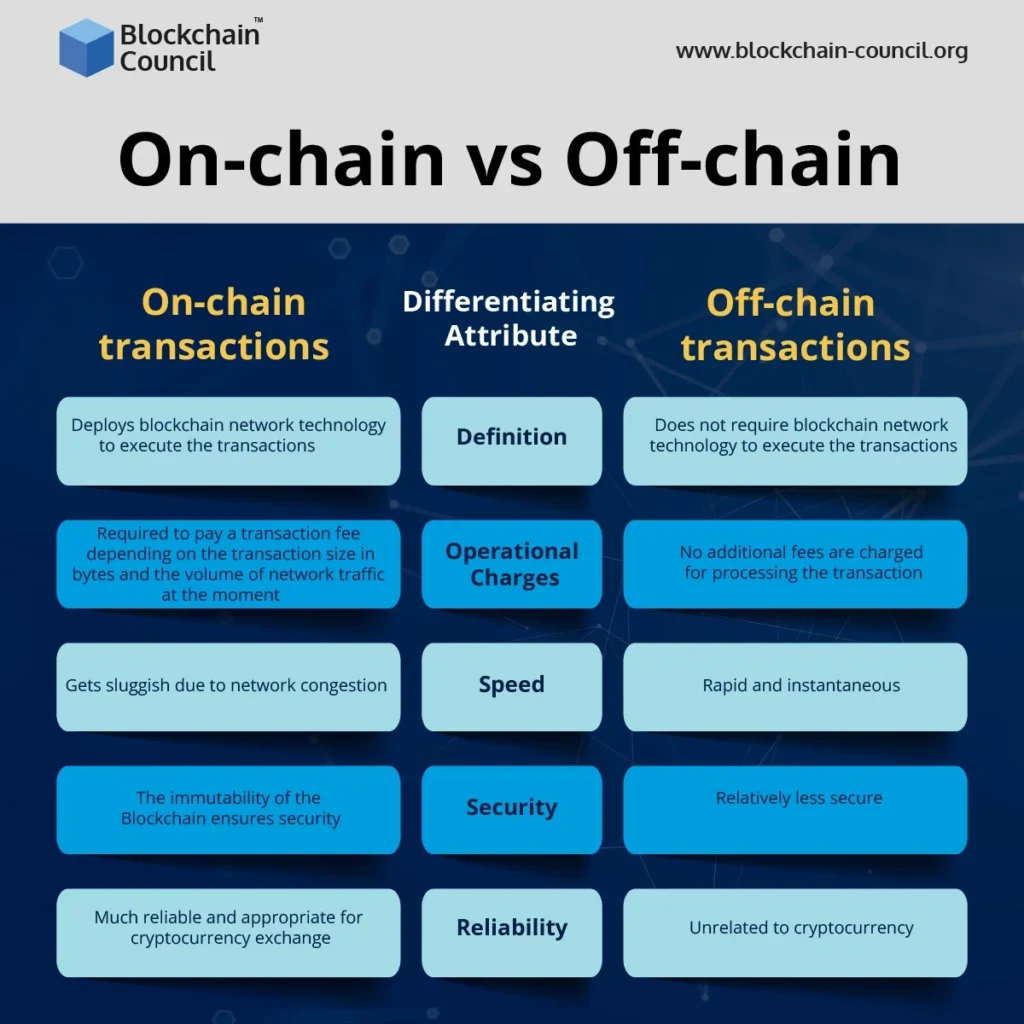
On-chain transactions occur directly on the blockchain. When a user initiates an on-chain transaction, it is broadcast to the network, where it undergoes validation through consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). Once validated, the transaction is added to a block and recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and immutability.
Advantages of On-Chain Transactions
- Security and Transparency: Transactions are recorded on a public ledger, making them transparent and secure.
- Immutability: Once confirmed, transactions cannot be altered or reversed, providing a high level of trust.
- Decentralization: Eliminates the need for intermediaries, aligning with the decentralized ethos of blockchain.
Disadvantages of On-Chain Transactions
- Slower Processing Times: Validation and confirmation can take time, especially during network congestion.
- Higher Transaction Fees: Due to the computational resources required for validation, fees can be higher.
- Scalability Issues: As the blockchain grows, processing times and fees may increase.
What Are Off-Chain Transactions?
Credit from Webopedia
Off-chain transactions occur outside the main blockchain network. These transactions are not immediately recorded on the blockchain but may be later settled or recorded through secondary channels or layer-2 solutions. Off-chain methods aim to improve scalability and reduce costs.
Advantages of Off-Chain Transactions
- Faster Processing: Transactions can be completed quickly without waiting for blockchain validation.
- Lower Fees: Reduced need for computational resources leads to lower transaction costs.
- Scalability: Enables handling of a higher volume of transactions without burdening the main blockchain.
Disadvantages of Off-Chain Transactions
- Reduced Security: May rely on centralized intermediaries, introducing potential points of failure.
- Lack of Immutability: Transactions may be altered or reversed, depending on the off-chain solution.
- Potential for Disputes: Without a public ledger, resolving conflicts can be challenging.
A Comparative Overview between Them
| Feature | On-Chain Transactions | Off-Chain Transactions |
|---|---|---|
| Security | High (due to blockchain validation) | Variable (depends on off-chain method) |
| Speed | Slower (due to network consensus) | Faster (no need for blockchain validation) |
| Cost | Higher (due to transaction fees) | Lower (reduced computational resources) |
| Transparency | Publicly recorded on blockchain | Not immediately recorded on blockchain |
| Immutability | Transactions are permanent | May be subject to change or reversal |
| Scalability | Limited by blockchain capacity | Higher, as transactions are processed off-chain |
Use Cases for On-Chain Transactions
On-chain transactions are ideal for scenarios where security, transparency, and immutability are paramount. Common use cases include:
- Large Asset Transfers: Transferring significant amounts of cryptocurrency or assets where security is a top priority.
- Smart Contracts: Executing decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts that require verifiable and irreversible transactions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Situations where a transparent and auditable record is necessary for compliance purposes.
Use Cases for Off-Chain Transactions
Off-chain transactions are suitable for applications requiring speed and cost efficiency. Typical use cases include:
- Microtransactions: Small-value transactions that would be uneconomical on-chain due to high fees.
- Gaming and NFTs: In-game purchases and non-fungible token (NFT) transfers that benefit from reduced transaction times and costs.
- Layer-2 Solutions: Implementations like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin or Optimistic Rollups for Ethereum that facilitate off-chain transactions.
Conclusion

Credit from B2BinPay
Understanding the differences between on-chain vs off-chain transactions is essential for navigating the cryptocurrency landscape. On-chain transactions offer unparalleled security and transparency, making them suitable for high-value and compliance-sensitive applications. Conversely, off-chain transactions provide speed and cost efficiency, catering to scenarios where these factors are prioritized. By evaluating the specific requirements of each use case, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions on the appropriate transaction method to employ.



